WAML Pre-Conference Workshop: OpenIndexMaps
QGIS
QGIS is a free, open-source desktop application for mapping and geospatial analysis. It is a volunteer-driven project with contributers from around the world. It reads and writes nearly every possible GIS data format, and has many features that are particularly useful for creating OpenIndexMaps GeoJSON files.
For this workshop, we recommend using version 3.28.5 Firenze LTR. LTR stands for Long Term Release and means that the QGIS developer community has committed to maintaining this version for a longer time, even as newer versions are released.
A quick tour of QGIS:
- Identify tool
 lets you look at a feature’s attributes
lets you look at a feature’s attributes - Layer Styling panel

- Selection tools are useful for running processing tools on subsets,
or saving subsets as new layers
 and
and 
- Processing toolbox
 contains hundreds of tools, including tools from other open-source GIS programs
like GDAL and GRASS
contains hundreds of tools, including tools from other open-source GIS programs
like GDAL and GRASS - Over 600 plugins written by QGIS users provide a wide range of additional functionality
CRS (coordinate reference system)
QGIS, like most open-source GIS programs, uses standard EPSG codes for coordinate systems and map projections.
- EPSG codes uniquely identify a CRS. For example:
- EPSG:4326 = WGS 84 (standard latitude/longitude)
- EPSG:3857 = WGS 84 / Pseudo-Mercator
- EPSG:32610 = WGS 84 / UTM zone 10N
- Hover over a layer name to see its CRS code
- If a CRS is missing or incorrect, right-click the layer name > Set CRS > Set Layer CRS…a
- But if the CRS is correct, and you want to transform the existing coordinates to another CRS:
- Use the Reproject Layer tool
- Or just specify a new CRS when saving to a new file (right-click layer name > export)
- Project CRS (i.e. the map projection) is identified in lower-right corner
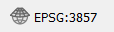
- Click it to change the Project CRS
- Or right-click a layer name > Set CRS > Set Project CRS from Layer
QuickMapServices
QuickMapServices is one of the most popular plugins. It provides access to basemaps from OpenStreetMap, Google, Bing, Esri, and more. Basemaps are useful for adding context to your maps, or to make sure that your data is showing up in the right place.
To install the plugin:
- Plugins menu > Manage and Install Plugins…
- Click the “All” tab at left
- Type in the search box “quickm” (you don’t have to type the whole name)
- Click the name “QuickMapServices” in the results
- Click “Install Plugin” (it only takes a few seconds)
Each plugin works a bit differently – some add menus items, some add tool buttons.
QuickMapServices appears under the “Web” menu.
It comes with a few basemaps, but you’ll want to add the full set of available basemaps:
- Web menu > QuickMapServices > Settings
- Click the “More services” tab
- Click “Get contributed pack”
Next: Exercise 1